2021.10.26
















magazine
2021.10.26

The key concept for Kyoto Experiment Autumn 2021 is “moshi moshi?!” Due to the pandemic online dialogues have become more frequent and we often find ourselves addressing an absent body that does not exist in the same space. Should we not therefore ask, how to listen to the voices of others who are / are not here and the sounds that are / are not currently occurring. Who is the subject that calls out “moshi moshi?!”, or is one being called? And how do you imagine the invisible on the other side of “moshi moshi?!” The next pages feature articles from a variety of different perspectives, all using the key concept “moshi moshi?!” as a starting point.
During the coronavirus pandemic, web conferencing tools like Teams and Zoom have become widespread, allowing us to hold meetings or classes remotely while still seeing each other’s faces, though more than a few people prefer to turn their camera off. If face to face, we can check emotional changes and the extent to which someone understands from their body language or facial expression, but when the face is not visible, everything hinges on the voice that is audible. Our sense of hearing then becomes accordingly acute. This makes us newly aware that communication quality is greatly dependent not only on the actual information that is relayed, but also on the “facial expression” of the voice that appears in the way something is said, volume, intonation, and tempo.
At call centers and such customer service providers, staff undergo instruction in improving their voice’s “facial expression” that exceeds technical training for how to speak in a voice that is easy to hear. This is founded upon the understanding that consideration for who you are speaking to, politeness, and quick-wittedness give your voice a “facial expression.” To put this another way, though we can actually change any voice through training, there endures the essentialist view that a telephone operator is always a woman, who is synonymous with possessing a “nice” voice that is easy to hear.
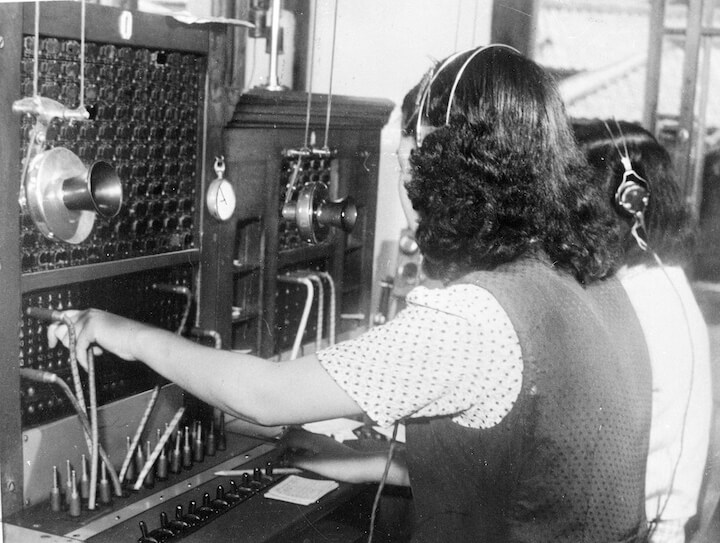
We now think nothing of calling and speaking to someone on the phone, but until telephones became automated a manual switchboard operator would connect the caller with whomever they were calling. Because of what these operators would first say to a caller, they became known in English-speaking countries as “hello girls” or in Japan as “moshi moshi girls” (after moshi moshi, the expression used when answering the phone). Since it was a new occupation pioneered mainly by middle-class women, the image of an operator as a woman’s job remains ingrained, though it was initially done by men. Why did women later gradually take over the role? The female voice was often cited as a reason that made women more suitable than men as switchboard operators. To the politicians who opposed hiring women as operators in the German Reichstag from the late nineteenth to early twentieth centuries, the undersecretary of the Ministry of Communications emphasized women’s aptitude for the job by linking the higher pitch of a woman’s voice with being easy to hear and sounding nice. But this is a leap of logic. A voice that is easy to hear does not necessarily sound “nice.”
The philosopher Walter Benjamin, who spent his childhood in Berlin at this time, describes the technical glitches during the early days of the telephone and how the telephone exchange and operators dealt with the complaints of users arising from these. Problems with the technology meant that telephones frequently failed to connect and users turned their fury first on the switchboard operator and then the telephone company itself. Given that many of the users at the time were men with a high social status, what could be done to keep their anger in check at this initial stage? In Japan too during the same period, it is said that male switchboard operators would give as good as they got verbally, leading to arguments with customers. The choice of operators ultimately fell on well-bred, unmarried young women, who were perceived as placid and, moreover, the kind of person with whom users would be reluctant to lose their temper. Their “nice” voice was, in fact, an amalgam of various elements, not least the way of speaking and attitudes expected of higher-class women and the expectations of users toward unmarried young women.
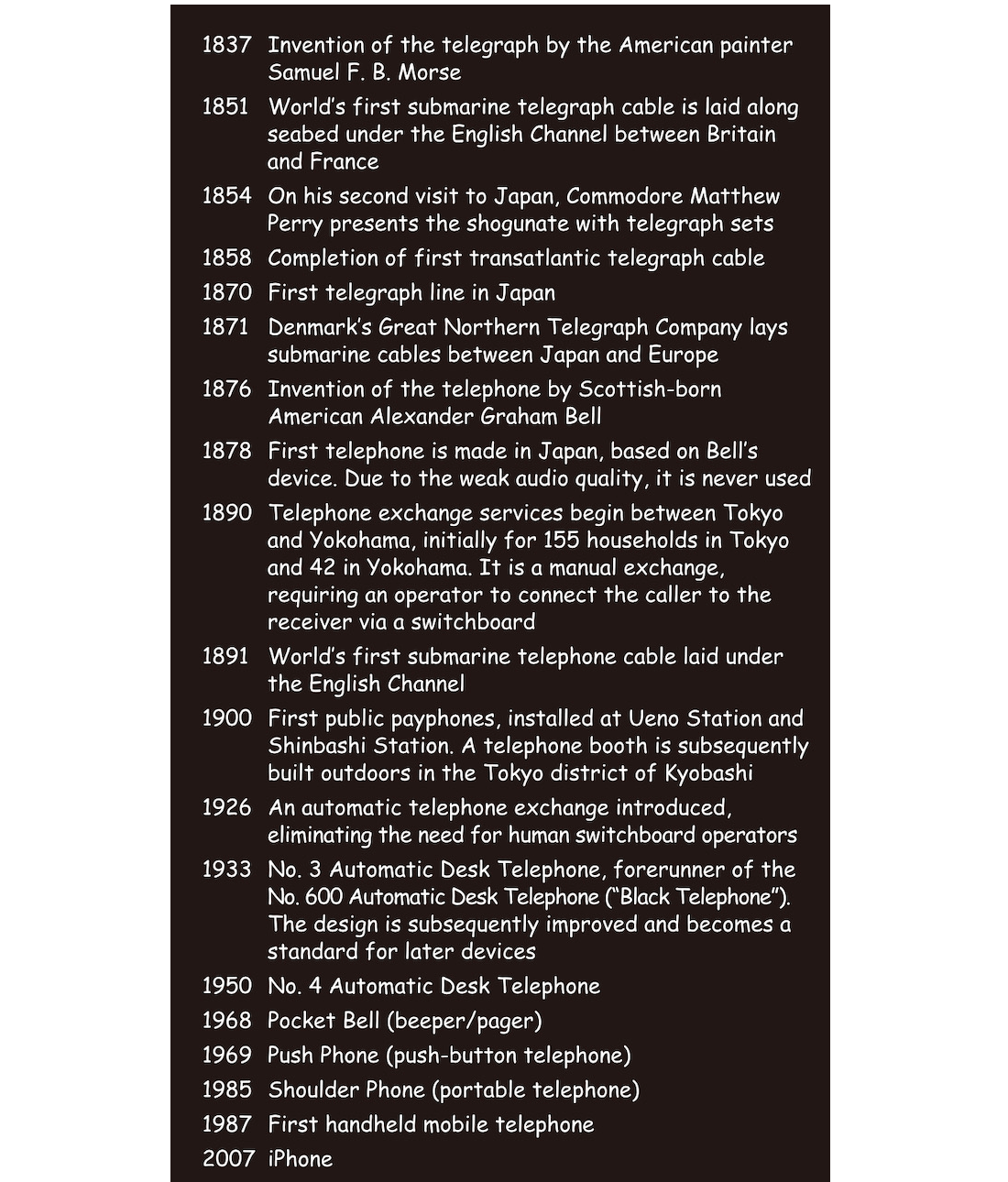
☝️ History of the Telegraph and Telephone
Timeline supervision, commentary: Kae Ishii
Online Resources
History of NTT
https://group.ntt/en/group/history/
150 Years of the Telephone in Japan: Looking Back on Telephone History, including the Black Telephone and Payphones
https://time-space.kddi.com/it-technology/20191023/2765
☎️Historical Background☎️
Humans have racked their brains to contrive means of relaying information over large distances. From drums to smoke signals, beacons, bells, signal guns, flag semaphore, carrier pigeons, and optical telegraphy, various methods were devised for conveying signals or words to faraway locations. Advances in industrialization and imperialism from the nineteenth century, in particular, ushered in striking developments in information and communications technology. With the appearance of telegraphy, a way of communicating that uses electricity, followed by the telephone, it became possible for information to reach distant places instantly in the form of signals or voices. The expansion of railroad networks, the opening of the Suez Canal, and the improvement of steamer ship routes, in addition to laying transatlantic telegraph cables, all accelerated the movement of people, things, and information, and hastened global integration.
Telegraph devices capable of transmitting and receiving Morse code were not only used by those in power seeking to exploit conflicts like the Satsuma Rebellion or Boxer Rebellion. They also rapidly relayed global news to boost economic activities and inspire ethnic identity around the world. On the other hand, in the sense that it could transmit an actual voice in real time, the telephone was revolutionary and became a commonplace means of communication we now use on an everyday basis. With the development and spread of information appliances and devices like mobile phones and smartphones since the end of the twentieth century, it became possible to send and receive not only voices but also text, pictures, and video, greatly furthering the compression of time and space.
Kae Ishii
Kae Ishii is an associate professor at the Doshisha University Faculty of Global and Regional Studies. A specialist in social history and gender history, her research particularly focuses on gender and labor in modern and contemporary Germany and Japan. Her publications include Why Did the Telephone Operator Become a Woman’s Job? A Comparative Social History of Technology and Gender in Japan and Germany (2018).